NAFCU to House Small Business Committee: EMV Not a ‘Silver Bullet’ to Broader Problem of Data Security
Washington (Oct. 7, 2015) – State Department Federal Credit Union President and CEO Jan Roche will testify today on behalf of the National Association of Federal Credit Unions (NAFCU) before a House Small Business Committee hearing on how credit unions are protecting consumers in the payment system, the impact of the EMV transition and what steps are needed to better protect consumer financial data moving forward. Roche is telling lawmakers that EMV “is not a ‘silver bullet’ to the broader solution of data security” and is urging action from Congress to enact H.R. 2205, the “Data Security Act of 2015.”
“NAFCU urges Congress to modernize data security laws to reflect the complexity of the current environment and insist that retailers and merchants adhere to a strong federal standard in this regard,” Roche says in her prepared testimony.
Roche, whose credit union is headquartered in Alexandria, Va., is testifying before the House Small Business Committee in today’s hearing, “The EMV Deadline and What it Means for Small Businesses,” which began at 11 a.m. Eastern.
NAFCU’s Participation in Data Security and Cyber Initiatives
Roche highlights NAFCU’s involvement in various industry and government payments, data security and cyber initiatives. NAFCU is a member of the Payments Security Task Force, a diverse group of participants in the payments industry that is driving a discussion on payments system security. NAFCU is also a member of the Financial Services Sector Coordinating Council and the Financial Services Information Sharing and Analysis Center, which work on infrastructure cybersecurity.
The EMV Transition
The EMV transition deadline established by the four major U.S. credit card issuers (Mastercard, Visa, Discover and American Express) was Oct. 1 of this year. Roche says that her credit union “was an early adapter to the U.S. transition, first issuing EMV cards in June of 2012 for new cards and replacements for lost and stolen cards. Our credit card portfolio of over 28,000 cards is now 100 percent EMV.”
“It is important to note that the EMV transition in the U.S. is a voluntary one established by the market, and not a government mandate,” says Roche. Consumers remain protected in the new system as “all credit cards have zero-liability provisions for consumers, and the Electronic Funds Transfer Act limits consumer liability for any fraud on debit cards.”
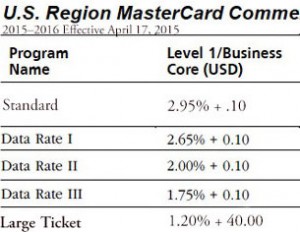
A NAFCU study of its members found that a majority of credit unions are ready for the EMV transition and are issuing EMV credit cards to members as they issue new cards or replace oldmagnetic strips. “There is a greater cost for an EMV card for credit unions,” Roche says. She states that at her credit union, the cost (not including staff costs, set-up and postage) to produce a non-EMV card is approximately $3.04 and to produce a new EMV card it is approximately $5.81.
A study released by the Strawhecker Group on Sept. 17 of this year reported only 27 percent of merchants were going to meet the EMV deadline. “We believe that successful protection of the payments system requires all parties to be actively involved and hope that these businesses will work with the financial services community to recognize their role in making the payments system safer,” says Roche.
The PIN Debate
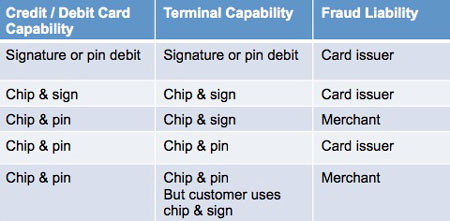
Roche discusses the debate among some that the EMV transition should have included a PIN mandate so consumers would be required to enter PINs for each transaction. “Imposing such a mandate or requirement would be unrealistic and would not be a panacea for the problem of data security,” Roche says. “It is the chip technology that makes new cards secure, not the PIN or signature.”
Roche states, “A truly secure payments system must be one that is constantly evolving to meet emerging threats and uses a wide range of dynamic authentication technologies – EMV, tokenization, encryption, biometrics and more.”
Credit Unions and Consumers Suffer from Data Breaches
A survey of NAFCU-member credit unions found that respondents were alerted to potential breaches an average of 164 times in 2014; two-thirds of respondents said they saw an increase in these alerts from 2013. In response to merchant data breaches that took place last year, 88.5 percent of credit union respondents said they notified a member; 65.4 percent issued new cards at a member’s request; and 57.5 percent placed a fraud alert on a member’s account.
“A credit union faces potential fines of up to $1 million per day for compliance violations,” says Roche. “In contrast, retailers are not covered by any federal laws or regulations that require them to protect the data and notify consumers when it is breached.”
Consumers are also the victims of data breaches. “Data security breaches are more than just an inconvenience to consumers as they wait for their plastic cards to be reissued,” says Roche. “Breaches often result in compromised card information leading to fraud losses, unnecessarily damaged credit ratings, and even identity theft.”
Credit Unions and the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
Credit unions and financial institutions have been subject to strict data security standards since the passage of the Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act in 1999. “Under the rules promulgated by the NCUA, every credit union must develop and maintain an information security program to protect customer data,” says Roche. “Additionally, the rules require third-party service providers that have access to credit union data take appropriate steps to protect the security and confidentiality of the information.” Roche states the “GLBA and its implementing regulations have successfully limited data breaches among credit unions.”
Preventing Future Data Breaches
NAFCU has long argued for a national data security standard for retailers and merchants similar to what credit unions already comply with under the GLBA. In addition, NAFCU has developed a number of key principles that should be considered and incorporated into the data security debate. These include:
Payment of breach costs by breached entities
National standards for safekeeping information
Data security policy disclosure
Notification of the account servicer
Disclosure of breached entity
Enforcement of prohibition on data retention
Burden of proof in data breach cases
While some have argued that voluntary industry standards should be the solution, the recently released Verizon 2015 Payment Card Industry Compliance Report found that four out of every five global companies fail to meet the widely accepted Payment Card Industry (PCI) data security standards for their payment card processing systems.
Legislative Solutions
NAFCU urges Congress to support H.R. 2205, the “Data Security Act of 2015,” introduced by Reps. Randy Neugebauer, R-Texas, and John Carney, D-Del. This bipartisan legislation “creates a national data security standard that is flexible and scalable, does not mandate static technology solutions and recognizes those who already have a working standard under the GLBA,” Roche says.
The National Association of Federal Credit Unions is the only national trade association focusing exclusively on federal issues affecting the nation’s federally insured credit unions. NAFCU membership is direct and provides credit unions with the best in federal advocacy, education and compliance assistance.www.nafcu.org.
###