EMV terminal selection directly impacts interchange rate qualification, the bulk of credit card processing fees.
November 4, 2015– EMV, short for Europay, MasterCard,Visa, chip card terminals are in high demand, short supply, and most likely an unwelcome expense. Building material suppliers go to great lengths to negotiate with their payment processors for reduced rates, but this approach only impacts a fraction of costs. There is much bigger value is managing the entire payment process to affect the biggest component of fees – card interchange. The EMV terminal implemented will directly impact interchange rate qualification, and none of the most popular terminals recommended today meet critical lumber and building supply requirements.
Interchange rates are non-negotiable, but they can be influenced. There are hundreds of fees that can be tacked on based on each transaction type. Due to complexities, building material suppliers must have an intelligent solution to manage the payment process and ensure compliance with all the rules.
PURCHASING CARDS
To qualify for the lowest interchange rates, transactions must meet all the rules for the specific card and transaction method. For building material suppliers business to business (B2B), processing level III data for Corporate, Purchasing, and Business cards is critical. Their card use is growing and savings of 90 basis points or more for some cards is an attractive margin difference worth achieving.
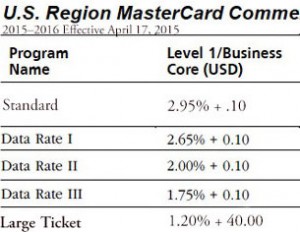
Sample interchange rates for the same credit card transaction; Failing to follow rules results in costly extra fees.
Countertop terminals like the popular First Data FD Series, Verifone VX series, or Ingenico iCT series, with downloaded programming, cannot support level III. The US EMV ecosystem requires a web-based payment gateway with EMV terminal and level III retail certification. For example, CenPOS has certified the Verifone MX915 to First Data, Chase Paymentech and Tsys, the latter which enables use with most processors. Merchants can use CenPOS via a web browser virtually instantly or an integrated application.
EMV COMPLIANCE DATES
While EMV is not a mandate, effective October 1, the party that does not support EMV (short for Europay, MasterCard, Visa) chip card acceptance is liable for counterfeit card, and sometimes lost or stolen card transactions. Because card issuers previously absorbed most of these losses without any notification to the merchant, businesses can expect losses if action is not taken. Additionally, non-EMV compliance fees have already been announced by at least one provider, NPC, starting January 1, 2016.
Christine Speedy, CenPOS global sales and integrated solutions reseller, 954-942-0483. CenPOS is a merchant-centric, end-to-end payments engine that drives enterprise-class solutions for businesses, saving them time and money, while improving their customer engagement. CenPOS? secure, cloud-based solution optimizes acceptance for all payment types across multiple channels without disrupting the merchant?s banking relationships.
